Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi
Isotope News, (786), p.26 - 29, 2023/04
no abstracts in English
Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki; Shimizu, Kazuyuki; Sugiyama, Takayuki
JAEA-Review 2021-008, 112 Pages, 2021/07
We had drastically been improving quality assurance system for Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), through applying new regulatory requirements, giving up ISO certification from FY2012 to 2019. In revising QA system, it is obviously necessary to satisfy the regulatory requirements, but it is important to continuously improve the QA system considering effectiveness to safety performance based on earlier experiences. In this report, the background of QA system revision, interpretation and thinking way of conformation and application to new regulation and "Application Guide to Quality Assurance Code for Safety in Nuclear Power Plants (JEAC 4111)" to TRP, issues considered. And matters that require attention for future QA activities are described. Key points are "in work processes planning, relationship with other sections and responsibility boundaries should be clearly defined with such as flow chart", "to manage decision-making processes is important, including input information, judgment criteria and so on", "concerning process monitoring and measurement, not only focusing on scheduling but also viewpoints toward conditions of facilities/systems, conformance to regulatory requirements and process improvement are necessary", and "in documentation, matching for existing system, clear relation to other fundamental documents are necessary".
Watanabe, Yusuke; Hayashida, Kazuki; Kato, Toshihiro; Kubota, Mitsuru; Aosai, Daisuke*; Kumamoto, Yoshiharu*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-002, 108 Pages, 2018/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigating groundwater chemistry to understand the effect of excavation and maintenance of underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in Mizunami, Gifu, Japan. In this report, we compiled data of groundwater chemistry and microbiology obtained at the MIU in the fiscal year 2016 and 2014 to 2016, respectively. In terms of ensuring traceability of data, basic information (e.g. sampling location, sampling time, sampling method and analytical method) and methodology for quality control are described.
Waste Technical Standards Working Group
JAEA-Review 2017-017, 112 Pages, 2017/11
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency, JAEA, a Waste Technical Standards Working Group has established since FY2015. The Working Group is composed of the members from waste management sections in each site in JAEA and from Radioactive Waste Management and Disposal Project Department. In this Working Group, we discussed quality management on conditioning waste packages, methodologies to evaluate the radioactivity concentration and measures for dismantling waste. This annual report summarizes the results of discussion in FY2016.
Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 22, 4 Pages, 2017/05
In the development of the simulation code and the numerical estimation for high cycle thermal fatigue on a structure caused by thermal striping phenomena in sodium cooled fast reactors, implementation of verification and validation (V&V) process is indispensable. A procedure named V2UP (Verification and Validation plus Uncertainty quantification and Prediction) has been made by referring to the existing guidelines regarding the V&V and the methodologies of the safety assessment. In this paper, a challenging installation of quality management procedures into the V2UP procedure is attempted based on the JSCES Standard for "A Model Procedure for Engineering Simulation".
Usuda, Shigekazu
Isotope News, (617), p.20 - 24, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
 accountancy and quality assurance
accountancy and quality assuranceKikuchi, Masahiro*; Muraoka, Susumu*; Osabe, Takeshi*; Terada, Hiromi; Shimizu, Kenichi; Otani, Tetsuo*; Fujimaki, Kazunori*; Ishikawa, Tadatsugu*; Shinohara, Yoshinori*
Dai-23-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu, p.91 - 98, 2002/12
Nuclear material measurement is an important measure to determine the amount of nuclear material of each stage such as receipt, shipment, inventory and hold-up. The material accountancy based on the material balance among the measurements is a measure to control of nuclear material. The material accountancy, from its technical aspect, can be used as promising measures for purposes from operator's level to state's level such as the nuclear safety, property control and environmental preservation other than safeguards measures only to conclude no diversion of nuclear material. This paper discusses various purposes of nuclear material measurements and clarifies the certain function to be expected at each purpose. Based on the discussion, critical points for the quality assurance of each stage are studied.
Yonezawa, Chushiro; Matsue, Hideaki; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Suzuki, Daisuke; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Inagawa, Jun; Saito, Yoko
Jitsuyo Gamma-sen Sokutei Handobukku, 366 Pages, 2002/06
no abstracts in English
Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8440 2001-023, 110 Pages, 2001/12
The business of the Safety administration Division became a wide range such as the management of a labor safety health, the crisis management, the security and the management of an entrance, and the business of the following concerning the Tokai Works, the protection of nuclear materials, the business of the sanction, the nuclear material safeguards, the transport of nuclear materials and the business of a quality assurance. For the purpose of summarizing these businesses and utilizing the data concerning the businesses, the report about the businesses achievement has been periodically drawn up as quarter news since 2001, when the Safety Administration Division was established. This report describes about the business achievement of the second quarter news from July to September in 2001.
Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8440 2001-015, 100 Pages, 2001/09
As a consequence of this reorganization, the business of the Safety Administration Division became a wide range such as the management of a labor safety health, the crisis management, the security and the management of an entrance, the business of the sanction concerning the Tokai Works, the protection of nuclear materials, the nuclear material safeguards, the transport of nuclear materials and the business of a quality assurance. In the respect of the purpose of summarizing these businesses and utilizing the data concerning the businesses, the report about a business achievement was determined to make.
 -irradiation on microflora and fermentation quality of silages containing tofu cake or brewer's gain
-irradiation on microflora and fermentation quality of silages containing tofu cake or brewer's gainTanaka, Osamu*; Akiyama, Fumiaki*; Yamada, Akihisa*; Ando, Sada*; Uegaki, Ryuichi*; Kobayashi, Ryoei*; Kume, Tamikazu
Nihon Sochi Gakkai-Shi, 47(3), p.274 - 282, 2001/08
no abstracts in English
Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Masuda, Shinichi; Yokoyama, Takashi*; Matoba, Toru; Nakajima, Kazuhisa
Proceedings of 26th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.132 - 134, 2001/08
no abstracts in English
 irradiation on microflora and fermentation quality of alfalfa, orchardgrass, maize and sorgum silage
irradiation on microflora and fermentation quality of alfalfa, orchardgrass, maize and sorgum silageTanaka, Osamu*; Akiyama, Fumiaki*; Yamada, Akihisa*; Ando, Sada*; Uegaki, Ryuichi*; Kobayashi, Ryoei*; Kume, Tamikazu
Nihon Sochi Gakkai-Shi, 47(1), p.62 - 67, 2001/04
no abstracts in English
Kojima, Takuji
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (89), p.4 - 7, 2001/01
This paper describes the present status of dosimetry as one of the useful technique for the process/quality control in radiation application and radiation research/testing. It introduces (a)activities in dose standardization of International Organization for Standardization(ISO) and International Atomic Energy Agency(IAEA) on publication of standards and organization of workshops, (b)recent efforts for consistency check in dose evaluation of electrons having energies above 4MeV, and (c)development status of dosimeter systems relevant to new requirements in dosimetry. It also comments on importance of planning for succession of high-dose dosimetry technology and education/training of dosimetry workers/researchers.
Kajiyama, Tadashi;
JNC TN8410 2000-015, 7 Pages, 2000/10
Some falsification has been detected in the results of quality control data relating to the diameter of samples of pellets produced in the BNFL's MOX Demonstration Facility (MDF) on September 1999. This document is the outlines of inspection procedure for the MONJU fuel pellet in plutonium fuel center of JNC.
Kakehi, Isao;
JNC TN9400 2000-054, 84 Pages, 2000/04
This report describes accomplishment of the study on the quality of vipac (vibro-packed) oxide fuel obtained by pyrochemical processing (molten salt electrolytic processing). This study is intended to contribute to the design study of the pyro-reprocessing-vipac fuel recycling system of oxide fuel. In this study, vibro-packing experiment has been conducted using granular U0 obtained by molten salt electrolytic processing (cold experiment). The oxide pyro process developed by Research lnstitute of Atomic Reactors (RIAR) is the method in which the sintered oxide is electrically deposited on the cathode at approximately 600
obtained by molten salt electrolytic processing (cold experiment). The oxide pyro process developed by Research lnstitute of Atomic Reactors (RIAR) is the method in which the sintered oxide is electrically deposited on the cathode at approximately 600 C. 0xide granules for vipac fuel are obtained by crushing the oxide deposited on the cathode. This process is also developed as recycle process because it is capable of FP separation. Also in Japan, this process is studied as one of the new FBR fuel recycling systems. ln this study, we made an effort to clarify the mechanisms of vibro-packing of the electrically obtained granules, which influence on the effective parameters of vibro-packing density and fuel particles size distribution in the fuel cladding in case of non-sphere particles of the granules. As a result of the study, smear density of 75% and almost uniform distribution of U0
C. 0xide granules for vipac fuel are obtained by crushing the oxide deposited on the cathode. This process is also developed as recycle process because it is capable of FP separation. Also in Japan, this process is studied as one of the new FBR fuel recycling systems. ln this study, we made an effort to clarify the mechanisms of vibro-packing of the electrically obtained granules, which influence on the effective parameters of vibro-packing density and fuel particles size distribution in the fuel cladding in case of non-sphere particles of the granules. As a result of the study, smear density of 75% and almost uniform distribution of U0 particles have been taken in the experiment, and much knowledge for the improvement of the vibro-packing quality has been found. And the possibility of the smear density over 80% and the uniform distribution of U0
particles have been taken in the experiment, and much knowledge for the improvement of the vibro-packing quality has been found. And the possibility of the smear density over 80% and the uniform distribution of U0 particles has been suggested in this study.
particles has been suggested in this study.
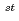 reload core fuel assembly
reload core fuel assemblyKajiyama, Tadashi; Numata, Kazuaki; Otani, Seiji; *; *; Goto, Tatsuro*; Takahashi, Hideki*
JNC TN8440 2000-008, 34 Pages, 2000/02
The procedure and result of lower endplug welding, Test and Inspection and Shipment of the 1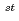 reload core fuel assembly (80 Fuel Assemblies) for the fast breeder reactor MONJU should be report, which had examined and inspected in Tamatsukuri Branch, Material Insurance office, Quality Assurance Section, Technical Administration Division, Plutonium Fuel Center (before: Inspection Section, Plutonium Fuel Division), from June 1994 to January 1996. The number of cladding tubes welded to the endplug were total to 13,804, 7,418 for Core - Inside of 43 fuel Assemblies and 6,386 for Core-Outside of 37 fuel Assemblies. 13,794 of them, 7,414 Core-Inside and 6,379 Core-Outside were approved by the test and sent to Plutonium Fuel Center. 10 of them weren't approved mainly because of default welding. Disapproval rating is 0.07%.
reload core fuel assembly (80 Fuel Assemblies) for the fast breeder reactor MONJU should be report, which had examined and inspected in Tamatsukuri Branch, Material Insurance office, Quality Assurance Section, Technical Administration Division, Plutonium Fuel Center (before: Inspection Section, Plutonium Fuel Division), from June 1994 to January 1996. The number of cladding tubes welded to the endplug were total to 13,804, 7,418 for Core - Inside of 43 fuel Assemblies and 6,386 for Core-Outside of 37 fuel Assemblies. 13,794 of them, 7,414 Core-Inside and 6,379 Core-Outside were approved by the test and sent to Plutonium Fuel Center. 10 of them weren't approved mainly because of default welding. Disapproval rating is 0.07%.
*; *; *; *; Sago, Hiromi*; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-049, 161 Pages, 2000/02
In this study basic data on welds of overpack structures for HLW were acquired and a predictive destruction analysis was performed usig the data acquired, in order to examine the viability of weld design methods. The results are summarized as follows: (1)Investigation of Design and Welding Condition for Welded Joint Models. Three welding methods--EBW, TIG and MAG--were selected, and welding conditions were determined so that the welding quality almost equivalent to that of an actual over-pack was ensured. (2)Fabrication of Welded Joint Models. Three welded joint models, one for each of EBW, TIG and MAG, were fabricated. It was confirmed that these models satisfied the quality requirements for Class I specified in JIS Z3104. (3)Sampling and Machining of Strength Test Specimens. Test specimens were taken from each welded joint model, and models for corrosion tests were delivered to the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC). (4)Strength Test and Micro/macro Structure observation. Tensile tests were conducted at room temperature and at 150 C, and fracture toughness tests at 0
C, and fracture toughness tests at 0 C and 150
C and 150 C, in order to obtain stress-strain curves, J-R curves and Vickers hardness. In addition, an observation of micro and macro structures was performed. (5)Evaluation. Using the data on the welds obtained from the tests, a fracture prediction analysis and an evaluation of unstable fracture due to weld flaws were performed on the over-pack design described in the second progress report. The following conclusions were obtained: (a)For the overpack design examined, the effects of welds (material property and residual stress) and fabrication tolerance on fracture loading are negligible. (b)In addition, it was decided that even in a design with reduced wall thickness, welds have an insignificant effect on fracture loading because fracture initiates in the center of the shell of the overpack. (c)The size of flaws leading to unstable fracture is on ...
C, in order to obtain stress-strain curves, J-R curves and Vickers hardness. In addition, an observation of micro and macro structures was performed. (5)Evaluation. Using the data on the welds obtained from the tests, a fracture prediction analysis and an evaluation of unstable fracture due to weld flaws were performed on the over-pack design described in the second progress report. The following conclusions were obtained: (a)For the overpack design examined, the effects of welds (material property and residual stress) and fabrication tolerance on fracture loading are negligible. (b)In addition, it was decided that even in a design with reduced wall thickness, welds have an insignificant effect on fracture loading because fracture initiates in the center of the shell of the overpack. (c)The size of flaws leading to unstable fracture is on ...
*; *; *; *; Sago, Hiromi*; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-048, 30 Pages, 2000/02
In this study basic data on welds of overpack structures for HLW were acquired and a predictive destruction analysis was performed using the data acquired, in order to examine the viability of weld design methods. The results are summarized as follows: (1)Investigation of Design and Welding Conditions for Welded Joint Models. Three welding methods--EBW, TIG and MAG-were selected, and welding conditions were determined so that the welding quality almost equivalent to that of an actual over-pack was ensured. (2)Fabrication of Welded Joint Models. Three welded joint models, one for each of EBW, TIG and MAG, were fabricated. It was confirmed that these models satisfied the quality requirements for Class I specified in JIS Z3104. (3)Sampling and Machining of Strength Test Specimens. Test specimens were taken from each welded joint model, and models for corrosion tests were delivered to the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC). (4)Strength Test and Micro/macro Structure observation. Tensile tests were conducted at room temperature and at 150 C, and fracture toughness tests at 0
C, and fracture toughness tests at 0 C and 150
C and 150 C, in order to obtain stress-strain curves, J-R curves and Vickers hardness. In addition, an observation of micro and macro structures was performed. (5)Evaluation. Using the data on the welds obtained from the tests, a fracture prediction analysis and an evaluation of unstable fracture due to weld flaws were performed on the over-pack design described in the second progress report. The following conclusions were obtained: (a)For the overpack design examined, the effects of welds (material property and residual stress) and fabrication tolerance on fracture loading are negligible. (b)In addition, it was decided that even in a design with reduced wall thickness, welds have an insignificant effect on fracture loading because fracture initiates in the center of the shell of the overpack. (c)The size of flaws leading to unstable fracture is on the ...
C, in order to obtain stress-strain curves, J-R curves and Vickers hardness. In addition, an observation of micro and macro structures was performed. (5)Evaluation. Using the data on the welds obtained from the tests, a fracture prediction analysis and an evaluation of unstable fracture due to weld flaws were performed on the over-pack design described in the second progress report. The following conclusions were obtained: (a)For the overpack design examined, the effects of welds (material property and residual stress) and fabrication tolerance on fracture loading are negligible. (b)In addition, it was decided that even in a design with reduced wall thickness, welds have an insignificant effect on fracture loading because fracture initiates in the center of the shell of the overpack. (c)The size of flaws leading to unstable fracture is on the ...
Ueta, Shinzo*; *; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-002, 364 Pages, 2000/02
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) have been setting migration parameters and developing its database for the 2nd Progress Report of HLW Geological Disposal (H12 Report). In this study, experimentswere carried out to certify the reliability of parameters and scenario, and examination was carried out to survey procedures of quality management. The main contents are as follows. (1)Data acquisition for certification of migration parameters. The effect of NH complex of Pd on distribution coefficients (Kd) of Pd on both bentonite and rocks, and the effect of sulfate and carbonate complexes of Am on Kds of Am on bentonite are investigated. Kds of Pd depended on NH
complex of Pd on distribution coefficients (Kd) of Pd on both bentonite and rocks, and the effect of sulfate and carbonate complexes of Am on Kds of Am on bentonite are investigated. Kds of Pd depended on NH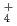 concentration in aqueous. The dependence varied with pH. Effects of sulfate and carbonate complexes on Kds of Am were not remarkable. Apparent diffusivities of Cs in bentonite saturated by saline water were measured. It was confirmed that the apparent diffusivities of Cs in saline water were similar to those in pure water. (2)Evaluation of colloidal effect on nuclide migration. An evaluation of validity of analytical model (Hwang's model) for nuclide migration under existence of colloids and investigation of characterization of colloids in groundwater were carried out. As the results, it was indicated that the Hwang's model was appropriate, and it was found that samplingtechnique influenced concentration and size distribution of colloids. (3)Influence of organic substances on solubility. Solubility of Th was measured under the condition with humic acid and carbonate. It increased roughly in proportion to the concentration of humic acid. And it was remarkably high under the condition with carbonate. It was confirmed that Th solubility data set in H12 report was conservative, even though humic acid existed in groundwater. (4)Use of Mechanistic Models for Safety Assessment. The integrated sorption/diffusion model has been used to calculate K
concentration in aqueous. The dependence varied with pH. Effects of sulfate and carbonate complexes on Kds of Am were not remarkable. Apparent diffusivities of Cs in bentonite saturated by saline water were measured. It was confirmed that the apparent diffusivities of Cs in saline water were similar to those in pure water. (2)Evaluation of colloidal effect on nuclide migration. An evaluation of validity of analytical model (Hwang's model) for nuclide migration under existence of colloids and investigation of characterization of colloids in groundwater were carried out. As the results, it was indicated that the Hwang's model was appropriate, and it was found that samplingtechnique influenced concentration and size distribution of colloids. (3)Influence of organic substances on solubility. Solubility of Th was measured under the condition with humic acid and carbonate. It increased roughly in proportion to the concentration of humic acid. And it was remarkably high under the condition with carbonate. It was confirmed that Th solubility data set in H12 report was conservative, even though humic acid existed in groundwater. (4)Use of Mechanistic Models for Safety Assessment. The integrated sorption/diffusion model has been used to calculate K , D
, D and D
and D values ...
values ...